Prerequisites
This page describes prerequisites for deploying COMAC, which includes:
- Hardware Requirements
- Connectivity Requirements
- Software Requirements
Before proceeding further, pelease read general CORD prerequisites first. This page addresses COMAC specific settings only based on the general requirements.
Hardware Requirements
Hardware requirements and COMAC BOM are described in this page.
Connectivity Requirements
Read this page first for the general connectivity requirements of CORD cluster. The same setup is applied when you run COMAC in a single cluster.
In a multi cluster setup such as the example setup below, you need to provide a method for inter-cluster communication for exchanging control packets between applications running on different cluster. There are various ways to achieve this requirement but we usually setup site-to-site VPN for the managment networks of the clusters.
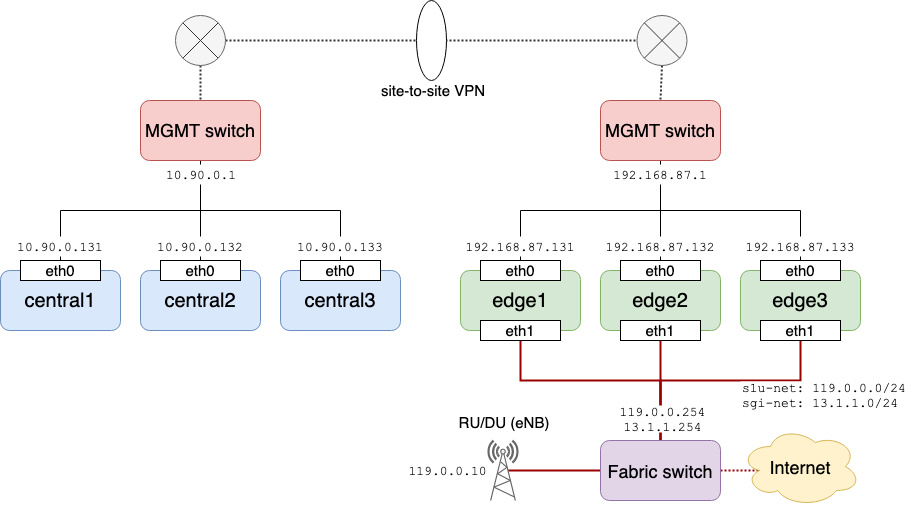
Note: COMAC currently only provides NodePort as a way to expose services outside
of the cluster. If two clusters in your environment are routed or reachable in
some way, there is no need to pay special attention.
Here is the list of default NodePort numbers that need to be opened externally
in case you want port forwarding.
| Cluster | Description | Default NodePort Number |
|---|---|---|
| Central | SPGWC-SPGWU communication | 30021 |
| Edge | SPGWC-SPGWC communication | 30020 |
| Central | CDN remote service HTTP UI | 32080 |
| Central | CDN remote service RTMP | 30935 |
Software Requirements
Node Setup
Operating System
COMAC runs on Kubernetes, so it will work on all Linux distributions. So far, Ubuntu 16.04 and 18.04 have been tested.
Enable SR-IOV
It is recommended to enable SR-IOV in a data plane interface for accellerating the data plane. Enabling SR-IOV includes:
- Enable VT-d
- Enable IOMMU
- Create VFs
- Bind VF to VFIO driver
The last step should be done only on the node that you want to run SPGWU. All data plane components in COMAC, SPGWU and CDN-local, support SR-IOV
but they require different type of drivers for the VFs.
SPGWU is implemented as a DPDK application so it requires VFs bounded
to VFIO driver, while CDN-local requires VFs bounded to normal kernel drivers.
We provide a script that automates all of the above steps.
Run node-setup.sh script with --vfio option to create VFIO bounded VFs.
$ git clone https://gerrit.opencord.org/automation-tools
$ cd automation-tools/comac/scripts/
$ sudo ./node-setup.sh -i [iface name] --vfio
OK: Intel VT is enabled
INFO: IOMMU is disabled
Added "intel_iommu=on" is to kernel parameters
INFO: Hugepage is disabled
Added "hugepages=32" is to kernel parameters
Added "default_hugepagesz=1G" is to kernel parameters
INFO: SR-IOV VF does not exist
Configured VFs on [iface name]
INFO: SR-IOV VF 0 does not exist or is not binded to vfio-pci
HINT: Grub was updated, reboot for changes to take effect
For VFs bounded to kernel driver, run the same command without --vfio option.
cd automation-tools/comac/scripts/
sudo ./node-setup.sh -i [iface name]
You'll need to reboot after running the script and run the script again after reboot to verify the settings.
$ sudo ./node-setup.sh -i [iface name] --vfio
OK: Intel VT is enabled
OK: IOMMU is enabled
OK: Hugepage is enabled
OK: SR-IOV is enabled on [iface name]
Kubernetes
Read this page first for a basic understanding of how to install Kubernetes in your environment. To run COMAC on Kubernetes, some additional settings are required.
- Enable
SCTPSupportas a feature gates - Install
MultusCNI plugin - Change NodePort range to
2000-36767
Here is an example Kubespray
configuration file that includes the additional settings listed above.
You can pass the file when running Kubespray ansible-playbook.
Note that it is tested with Kubespray version release-2.11.
$ cat >> extra-vars.yaml << EOF
# OS
disable_swap: true
populate_inventory_to_hosts_file: true
# etcd
etcd_deployment_type: docker
etcd_memory_limit: 8192M
# K8S
kubelet_deployment_type: host
kubectl_localhost: true
kubeconfig_localhost: true
kube_feature_gates: [SCTPSupport=True]
kube_apiserver_node_port_range: 2000-36767
kube_network_plugin: calico
kube_network_plugin_multus: true
multus_version: stable
local_volume_provisioner_enabled: true
# Applications
dns_mode: coredns
dns_cores_per_replica: 256
dns_min_replicas: 1
helm_enabled: true
helm_deployment_type: host
helm_version: v2.14.2
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -b -i inventory/comac/edge.ini -e @inventory/comac/extra-vars.yaml cluster.yml
We also provide sample Kubespray inventories and configuration files under automation-tools/comac/sample directory.
Once you have installed Kubernetes, the next step is to install CORD platform.
Refer to this page for the
basic instructions. For configuring nem-monitoring for COMAC, see this page.
Trellis for Fabric
You may use Trellis for configuring the data plane networks.
You'll need to create a Tosca configuration file for your networks and then push
the configurations to XOS. XOS exposes itself with NodePort, so you can
interface to it with one of the node IP in the cluster.
curl -H "xos-username: admin@opencord.org" \
-H "xos-password: letmein" -X POST \
--data-binary @comac-fabric.yaml \
http://<nodeIP>:30007/run
You can find the Tosca file for the example setup from here. See Trellis Fabric Documentation for more information.